CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Ex 7.3 || NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7: Coordinate Geometry(English Medium)
NCERT Class 10 Mathematics Chapter 7: Coordinate Geometry – For Free. || Get the complete NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7: Coordinate Geometry, covering Exercise 7.3. This free resource helps you understand key concepts and solve problems with ease, perfect for Class 10 students preparing for exams using NCERT Maths materials. We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Exercise 7.3 help you. If you have any queries regarding NCERT Maths Solutions Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Exercise 7.3, drop a comment below, and we will get back to you at the earliest.

CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Ex 7.3 || NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7: Coordinate Geometry(English Medium)
Exercise - 7.3
CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Ex 7.3 || NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7: Coordinate Geometry(English Medium)
Download the Math Ninja App Now1. Find the area of the triangle whose vertices are:
Area of triangle \( =\frac{1}{2}\left[x_{1}\left(y_{2}-y_{3}\right)+x_{2}\left(y_{3}-y_{1}\right)+x_{3}\left(y_{1}-y_{2}\right)\right] \)
For triangle given: \( \mathrm{A}(2,3), \mathrm{B}(-1,0), \mathrm{C}(2,-4) \)
Area of the triangle \( =\frac{1}{2}[2(0+4)-1(-4-3)+2(3-0) \) \( =\frac{1}{2}(8+7+6) \)
\( =\frac{21}{2} \) Square units
Area of triangle \( =\frac{1}{2}\left[x_{1}\left(y_{2}-y_{3}\right)+x_{2}\left(y_{3}-y_{1}\right)+x_{3}\left(y_{1}-y_{2}\right)\right] \)
For triangle given: \( A(-5,-1), B(3,-5), C(5,2) \)
Area of the triangle \( =\frac{1}{2}[-5(-5-2)+3(2+1)+5(-1+5) \) \( =\frac{1}{2}(35+9+20) \)
\( =32 \) square units
CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Ex 7.3 || NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7: Coordinate Geometry(English Medium)
Download the Math Ninja App Now2. In each of the following find the value of ' \( k \) ', for which the points are collinear
Area of triangle \( \mathrm{ABC}=\frac{1}{2}\left[x_{1}\left(y_{2}-y_{3}\right)+x_{2}\left(y_{3}-y_{1}\right)+x_{3}\left(y_{1}-\right.\right. \)
\( \left.\left.y_{2}\right)\right] \)
Collinear points mean that the points lie on a straight line. So, For collinear points, area of triangle formed by them is zero
Therefore, for points \( (7,-2)(5,1) \), and \( (3, k) \), area \( =0 \)
\( \frac{1}{2}[7(1-\mathrm{k})+5(\mathrm{k}+2)+3(-2-1)=0\)
\(7-7 \mathrm{k}+5 \mathrm{k}+10-9=0\)
\(-2 \mathrm{k}+8=0\)
\(\mathrm{k}=4 \)
Area of triangle \( \mathrm{ABC}=\frac{1}{2}\left[x_{1}\left(y_{2}-y_{3}\right)+x_{2}\left(y_{3}-y_{1}\right)+x_{3}\left(y_{1}-\right.\right. \)
\( \left.\left.y_{2}\right)\right] \)
For collinear points, area of triangle formed by them is zero.
Therefore, for points \( (8,1),(k,-4) \), and \( (2,-5) \), area \( =0 \)
\(\frac{1}{2}[8(-4+5)+\mathrm{k}(-5-1)+2(1+4)=0\)
\(8-6 \mathrm{k}+10=0\)
\(6 \mathrm{k}=18\)
\(\mathrm{k}=3 \)
CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Ex 7.3 || NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7: Coordinate Geometry(English Medium)
Download the Math Ninja App Now
We know, mid-points of a line joining points \( \left(y_{1}, y_{1}\right) \) and \( \left(x_{2}, y_{2}\right) \) is given by
\( \left(\frac{x_{1}+x_{2}}{2}, \frac{y_{1}+y_{2}}{2}\right) \)
Let \( \mathrm{D}, \mathrm{E}, \mathrm{F} \) be the mid-points of the sides of this triangle. Coordinates of \( \mathrm{D}, \mathrm{E} \), and F are given by
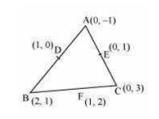
\( D=\left(\frac{0+2}{2}, \frac{-1+1}{2}\right)=(1,0) \)
\( E=\left(\frac{0+0}{2}, \frac{3-1}{2}\right)=(0,1)\)
\(F=\left(\frac{2+0}{2}, \frac{1+3}{2}\right)=(1,2) \)
Also, we know area of a triangle having \( \left(x_{1}, y_{1}\right),\left(x_{2}, y_{2}\right) \) and \( \left(x_{3}, y_{3}\right) \) is
\( \frac{1}{2}\left(x_{1}\left(y_{2}-y_{3}\right)+x_{2}\left(y_{3}-y_{1}\right)+x_{3}\left(y_{1}-y_{2}\right)\right) \)
Area of the triangle \( (\mathrm{DEF})=\frac{1}{2}[1(2-1)+1(1-0)+0(0-2) \)
\( =\frac{1}{2}(1+1) \)
\( =1 \) square unit
Area of the triangle \( (\mathrm{ABC})=^{\frac{1}{2}}[0(1-3)+2(3+1)+0(-1-1) \)
\( =\frac{1}{2} \times 8 \)
\( =4 \) square units
Therefore, required ratio \( =1: 4 \).
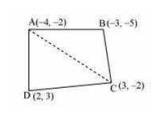
Area of the triangle \( (\mathrm{ABC})=\frac{1}{2}[-4(-5+2)-3(-2+2)+3(-2+5)] \) \( =\frac{1}{2}(12+0+9) \)
\( =\frac{21}{2} \) Square units
Area of the triangle \( (\mathrm{ACD})=\frac{1}{2}[-4(-2-3)+3(3+2)+2(-2+2)] \)
\( =\frac{1}{2}(20+15+0) \)
\( =\frac{35}{2} \) Square units
Area of Quadrilateral \( \mathrm{ABCD}= \) Area of the triangle \( (\mathrm{ABC})+ \) Area of the triangle \( (\mathrm{ACD}) \)
\( =\frac{21}{2}+\frac{35}{2} \)
\( =\frac{56}{2} \)
\( =28 \) Square units
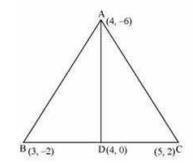
Let D be the mid-point of side BC of \( \triangle \mathrm{ABC} \)
Therefore, AD is the median in \( \triangle \mathrm{ABC} \)
To prove: Area \( \triangle \mathrm{ABC}= \) Area \( \triangle \mathrm{ABD}+ \) Area \( \triangle \mathrm{ADC} \)
Midpoint of the line joining the points \( A\left(x_{1}, y_{1}\right) \) and \( B\left(x_{2}, y_{2}\right) \) is given by
\( X=\frac{x_{1}+x_{2}}{2}, \frac{y_{1}+y_{2}}{2} \)
Therefore, by applying the formula we can get the coordinate of D Coordinate of point \( D=\left(\frac{3+5}{2}, \frac{-2+2}{0}\right)=(4,0) \)
We also know that if \( \mathrm{A}\left(x_{1}, y_{1}\right), \mathrm{B}\left(x_{2}, y_{2}\right) \) and \( \mathrm{C}\left(x_{3}, y_{3}\right) \) are vertices of a triangle then
Area of triangle is given by,
\( \text { Area }=\frac{1}{2}\left[x_{1}\left(y_{2}-y_{3}\right)-x_{2}\left(y_{3}-y_{1}\right)+x_{3}\left(y_{1}-y_{2}\right)\right] \)
For \( A(4,-6), B(3,-2) \), and \( C(5,2) \)
Area of the \( \Delta(\mathrm{ABC})=\frac{1}{2}[4(-2-2)+3(0+8)+5(-6+2)] \)
\( =\frac{1}{2}(-8+32-30) \)
\( =-3 \) Square units
However, area cannot be negative. Therefore, area of \( \triangle \mathrm{ADC} \) is 3 square units
Now for for \( A(4,-6), B(3,-2) \) and \( D(4,0) \) Area of \( \Delta A B D \) \( =\frac{1}{2}[4(-2-0)+3(0+6)+4(-6+2)] \)
Area \( =\frac{1}{2}[-8+18-16] \)
Area \( =-3 \) square units Now the Area cannot be negative so Area of \( \triangle \mathbf{A B D}=3 \) units
Area of \( \triangle \mathrm{ABD}+ \) Area of \( \Delta \mathrm{ADC}=3+3 \) square units
Area of \( \triangle \mathrm{ABD}+ \) Area of \( \Delta \mathrm{ADC}=6= \) Area of \( \triangle \mathrm{ABC} \)
Clearly, median AD has divided \( \triangle \mathrm{ABC} \) in two triangles of equal areas
CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Ex 7.3 || NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7: Coordinate Geometry(English Medium)
Download the Math Ninja App NowCentral Board of Secondary Education Official Site
Class 10 : NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.1
Class 10 : NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.2
Class 10 : NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.3
Class 10 : CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2.1
Class 10 : CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2.2
Class 10 : CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2.4
Class 10 : CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.1
Class 10 : CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 3: Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables || CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables solutions Ex 3.2
Class 10 : CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 3: Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables || CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables solutions Ex 3.3
Class 10 : CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 3: Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables || CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables solutions Ex 3.4
Class 10 : CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 3: Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables || CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables solutions Ex 3.5
Class 10 : CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 3: Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables || CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables solutions Ex 3.6
Class 10 : CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations Ex 4.1 || NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4: Quadratic Equations (English Medium)
Class 10 : CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations Ex 4.2 || NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4: Quadratic Equations (English Medium)
Class 10 : CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations Ex 4.3 || NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4: Quadratic Equations (English Medium)
Class 10 : CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions Ex 5.1
Class 10 : CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions Ex 5.2
Class 10 : CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions Ex 5.3
Class 10 : NCERT Math Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangle(English Medium) || CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangle Ex 6.1
Class 10 : NCERT Math Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangle(English Medium) || CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangle Ex 6.2
Class 10 : NCERT Math Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangle(English Medium) || CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangle Ex 6.3
Class 10 : NCERT Math Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangle(English Medium) || CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangle Ex 6.4
Class 10 : NCERT Math Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangle(English Medium) || CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangle Ex 6.5
Class 10 : NCERT Math Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangle(English Medium) || CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangle Ex 6.6
Class 10 : NCERT Math Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry(English Medium) || CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Ex 7.1
Class 10 : NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Exercise 8.2
Class 10 : CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles solutions Ex 10.2
Class 10 : CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes solutions Ex 13.2
